109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

细胞程序性死亡配体 1 抗体在胃肠道癌中的表达状态和预后意义:系统回顾和汇总分析
Authors Huang B, Chen L, Bao C, Sun C, Li J, Wang L, Zhang X
Received 24 June 2015
Accepted for publication 22 July 2015
Published 15 September 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 2617—2625
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S91025
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Dekuang Zhao
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Pietersz
Background: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression has been observed in various malignancies. However, the association between PD-L1 expression and the survival of patients with gastrointestinal tract cancer remains controversial. Besides, the rate of PD-L1 positivity on tumor cells of digestive tract cancer is not clear. Thus, we performed a meta-analysis by incorporating all available evidence to evaluate the rate of PD-L1 positivity and the overall survival (OS) according to PD-L1 status in patients with gastrointestinal tract cancer.
Methods: Electronic databases were searched for eligible literature. Hazard ratios (HRs) for OS with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) according to the expression status of PD-L1 evaluated by immunohistochemistry were extracted. The outcomes were synthesized based on a random-effects model.
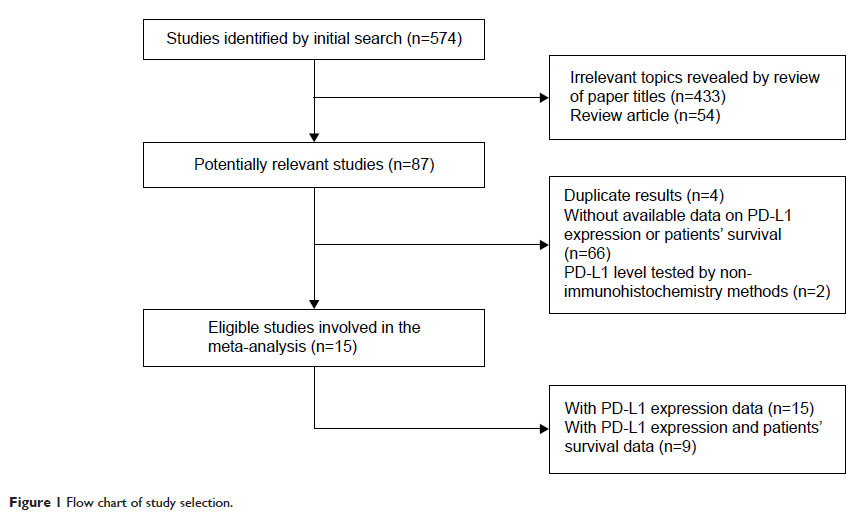
Results: Fifteen studies (only nine reported OS) that involved 2,993 gastrointestinal tract cancer patients stratified by PD-L1 status were eligible for inclusion in our study. We found the PD-L1-positive expression rate was 0.495 (95% CI 0.415–0.576) if 10% was taken as the cut-off value. When the H-score method was used to evaluate PD-L1 expression, it showed that the PD-L1 positive rate was 0.639 (95% CI 0.490–0.765) if the cut-off value was <50, which was higher than when using >50 as the cut-off point (0.449, 95% CI 0.417–0.483). Additionally, PD-L1-positive gastrointestinal tract cancer patients were associated with significantly poorer OS when compared to negative ones (HR 1.61, 95% CI 1.10–2.35, P =0.014). Subgroup analysis presented similar significant results in patients with esophageal cancer (HR 2.56, 95% CI 1.55–4.21, P <0.001).
Conclusion: The positive expression rate of PD-L1 was nearly 50% no matter which method for immunohistochemistry evaluation we chose. Additionally, positive PD-L1 expression status in tumor cells is a risk factor for prognosis of gastrointestinal tract cancer, especially esophageal cancer.
Keywords: prognosis, esophageal cancer, immunohistochemistry, PD-L1-positive expression rate