109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
对接受手术后化疗的结直肠癌患者的急性胰腺炎的临床分析
Authors Ji YL, Han Z, Shao LM, Li YL, Zhao L, Zhao YH
Received 19 May 2015
Accepted for publication 14 July 2015
Published 11 September 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 2527—2533
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S88857
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Dekuang Zhao
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Daniele Santini
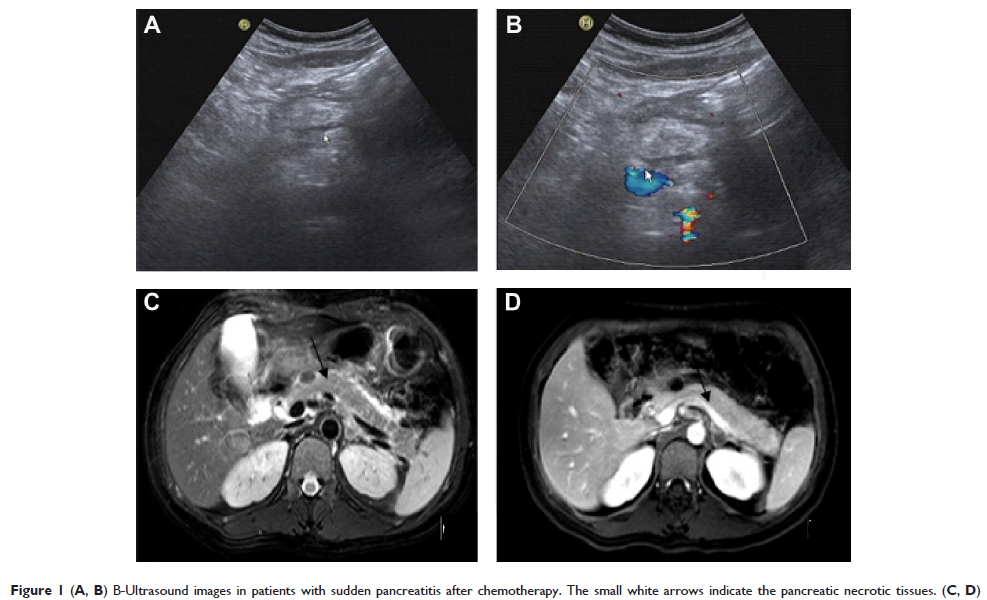
Abstract: Acute pancreatitis is a rare complication in postoperative colorectal cancer patients after FOLFOX6 (oxaliplatin + calcium folinate +5-FU [5-fluorouracil]) chemotherapy. In this paper, a total of 62 patients with gastrointestinal cancer were observed after the burst of acute pancreatitis. Surgery of the 62 cases of colorectal cancer patients was completed successfully. But when they underwent FOLFOX6 chemotherapy, five patients got acute pancreatitis (8.06%), four (6.45%) had mild acute pancreatitis, and one (1.61%) had severe acute pancreatitis, of which two were males (3.23%) and three females (4.84%). No patients (0.00%) had acute pancreatitis on the 1st day after chemotherapy; one patient (1.61%) got it in the first 2 and 3 days after chemotherapy; and three others (4.83%) got it in the first 4 days after chemotherapy. In the 62 patients with malignant tumors, the body mass index (BMI) was less than 18 (underweight) in six of them, with two cases of acute pancreatitis (33.33%); the BMI was 18–25 (normal weight) in 34 cases, with one case (2.94%) of acute pancreatitis; the BMI was 25–30 (overweight) in 13 cases, with 0 cases (0.00%) of acute pancreatitis; and the BMI was ≥30 (obese) in nine patients, with two cases of acute pancreatitis (22.22%). After symptomatic treatment, four patients were cured and one died; the mortality rate was 1.61%. Most of them appeared in the first 4 days after chemotherapy; the probability of this complication is significantly higher in slim and obese patients than in normal weight patients. Postoperative colorectal cancer patients after FOLFOX6 chemotherapy have a sudden onset of acute pancreatitis occult, especially in patients with severe acute pancreatitis; the symptoms are difficult to control, there is high mortality and it is worthy of clinician’s attention.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, postoperative, acute pancreatitis, chemotherapy
Keywords: colorectal cancer, postoperative, acute pancreatitis, chemotherapy