109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用长循环高分子脂质体载体向缺血/再灌注大鼠心肌进行麦冬多糖 (Radix Ophiopogonis polysaccharide) 的靶向给药
Authors Wang LN, Yao CX, Wu F, Lin X, Shen L, Feng Y
Received 28 May 2015
Accepted for publication 14 August 2015
Published 10 September 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 5729—5737
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S89445
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
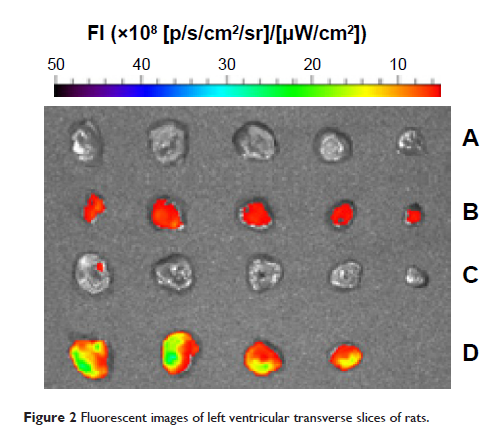
Abstract: Drug delivery to ischemic myocardium is an enormous challenge. This work aimed to characterize cardiac delivery behaviors of mono-polyethylene glycosylated (PEGylated) conjugates and long-circulating liposomes (L-Lps) with Radix Ophiopogonis polysaccharide (ROP) as drug. The results showed that compared to native ROP, 32-, 52-, and 45-fold increases in blood half-life were achieved by 20-kDa PEG mono-modified ROP (P20k-R), 40-kDa PEG mono-modified ROP (P40k-R), and ROP-loaded L-Lp, respectively. With comparable blood pharmacokinetics, ROP-loaded L-Lp showed both significantly higher targeting efficacy and drug exposure in infarcted myocardium than P40k-R. With regard to P20k-R, both its targeting efficacy and its level in infarcted myocardium at 3 hours postdose were comparable to P40k-R, but its level in blood and myocardium reduced obviously faster. As a whole, the results indicate that both loading in L-Lps and mono-PEGylation are effective in targeting drug to ischemic myocardium, but the former appears to induce stronger effects.
Keywords: PEGylation, liposome, myocardial targeting, Radix Ophiopogonis polysaccharide, fluorescent imaging