109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

P53 突变体 p53N236S 通过 Stat3 信号通路调节癌相关成纤维细胞的特性
Authors Liu Q, Yu B, Tian Y, Dan J, Luo Y, Wu X
Received 28 August 2019
Accepted for publication 10 January 2020
Published 14 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1355—1363
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S229065
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
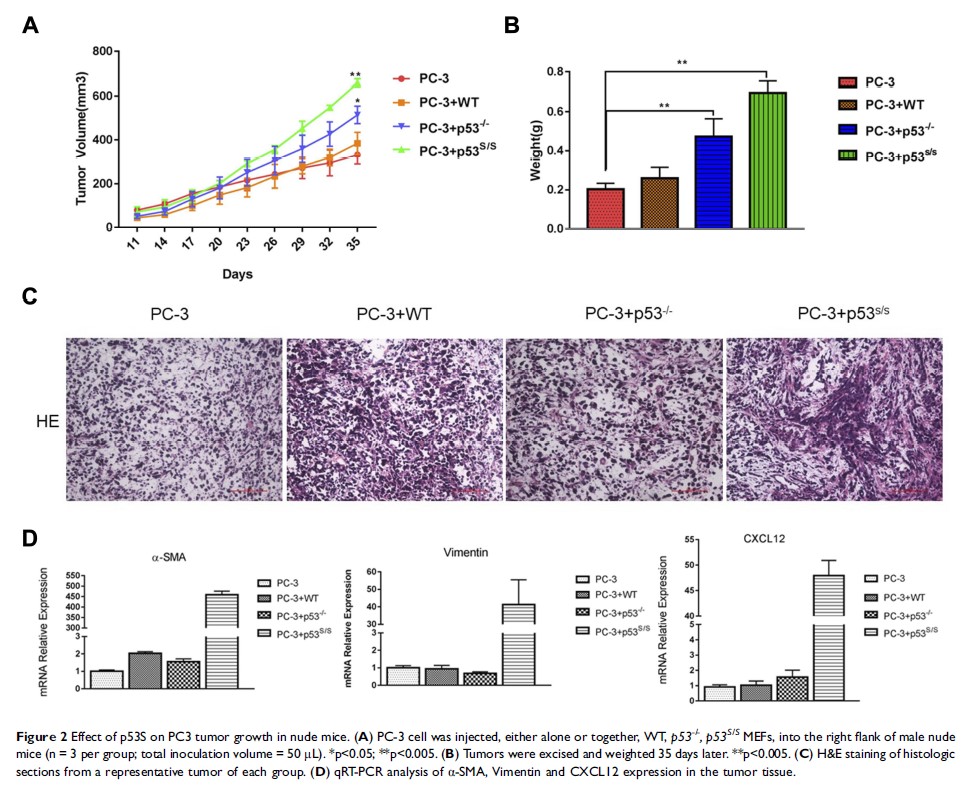
Background: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play important roles in cancer development and progression. Recent studies show that p53 plays a cell non-autonomous tumor-suppressive role to restrict tumor growth in CAFs. However, the role of p53 mutant in CAFs remains obscure.
Methods: In this study, the contribution of p53 mutant p53N236S (p53S) to CAFs activation was examined using mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) from wild-type (WT), p53 deficient (p53-/- ) and p53S/S mice. The role of p53S in MEFs in inducing prostate cancer cell growth and metastasis was studied by utilizing xenograft models and transwell assays. The effects of p53S on the properties of CAFs were assessed by measuring CAFs-specific factors expression and functional collagen contraction assay. Moreover, Microarray data were analyzed by GSEA and Stat3 signaling was inhibited to further determine p53S’s role in the CAFs activation.
Results: We found that p53S/S MEF accelerated cancer cells growth and metastasis compared with WT and p53-/- MEF. We also found that p53S induced significantly increasing collagen contraction in fibroblasts and overexpression of CAFs-specific factors, such as α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), FGF10 and CXCL12. p53S regulated these CAF-specific properties through Stat3 activation.
Conclusion: Our results illustrate that p53S plays an important role in CAFs activation by the Stat3 pathway. The study indicates that cancer cells and fibroblasts interaction promotes prostate cancer cell growth, migration and invasion due to p53S expression in fibroblasts.
Keywords: p53N236S, cancer-associated fibroblasts, Stat3 pathway